OSI 7 Layers
The English parts are content studied initially & the Korean parts are content studied again from books
Reference: [Book] Network Introduction for IT Engineers
Before getting started
In the past, communication protocols were not standardized, so there were many incompatible systems and applications, and communication was impossible
The effort to unify these into a single standard remains as today's
OSI 7 Layers!
Although
OSI 7 Layersis utilized as the main network reference model since it helps in understanding and developing network operations by dividing them,Currently most protocols are based on the TCP/IP protocol stack
What is OSI 7 Layers?
OSI 7 Layers
OSI (= Open Systems Interconnection) is a 7 layer architecture with each layer having specific functionality to perform.
All these 7 layers work collaboratively to transmit the data from one person to another across the globe.
The OSI 7 Layers can be divided into two categories based on the role and purpose of each layer.
Layers 1~4
Lower LayerData Flow LayerResponsible for delivering data to the other party
Layers 5~7
Upper LayerApplication LayerResponsible for creating data
Application developers
Focus on representing data without considering the data flow layer
View the network in a
Top-downmanner
Network engineers
Since the application layer is the domain application developers should consider, network engineers generally do not worry seriously about this area
View the network in a
Bottom-upmanner
Details
1. Physical Layer (Layer 1)
The lowest layer of the OSI reference model is the physical layer.
It is responsible for the actual physical connection between the devices.
The physical layer contains information in the form of bits.
It is responsible for transmitting individual bits from one node to the next.
When receiving data, this layer will get the signal received and convert it into 0s and 1s and send them to the Data Link layer, which will put the frame back together.
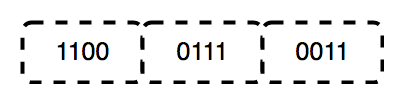
Defines information related to physical connections
Mainly focused on transmitting electrical signals
Since the goal is to transmit incoming electrical signals as-is, when an electrical signal enters a
Layer 1 device, it regenerates the electrical signal and sends it out
Layer 1 devices have no concept of addresses!
They transmit the same electrical signal to all ports except the port the signal came in on
In other words, source and destination cannot be distinguished
2. Data Link Layer (DLL) (Layer 2)
The data link layer is responsible for the node to node delivery of the message.
The main function of this layer is to make sure data transfer is error-free from one node to another, over the physical layer.
When a
packetarrives in a network, it is the responsibility of DLL to transmit it to the Host using itsMAC address.Data Link Layer is divided into two sub layers :
Logical Link Control (LLC)Media Access Control (MAC)
The packet received from Network layer is further divided into frames depending on the frame size of
NIC(Network Interface Card).DLL encapsulates Sender and Receiver's MAC address in the header.
The Receiver's MAC address is obtained by placing an
ARP(Address Resolution Protocol)request onto the wire asking "Who has that IP address?" and the destination host will reply with its MAC address.
Collects electrical signals and processes them into a recognizable data form
Unlike Layer 1, rather than precisely transmitting electrical signals, the focus is on defining
address informationand communicating to thecorrect addressChecks the
sourceanddestinationaddresses, verifies whether it was sent to me or whether I need to process it, and then performs data processingIn Layer 2, as the
address systemis introduced, functions for distinguishing between multiple simultaneous communications are primarily definedSince it collects
electrical signalsand processes them into data form, it can perform the role of detecting or correcting errors in dataIn Ethernet-based networks, Layer 2 only performs the role of detecting errors
Having an address system means communicating with multiple parties simultaneously rather than just one, so instead of blindly sending data, checking whether the recipient can currently receive data must be done first
This role is called
Flow ControlFlow Control
Server sends data to the switch
Congestion occurs at the switch. The switch sends a Pause frame to the server
The server waits after receiving the Pause frame
The network components of Layer 2 are
Network Interface CardandSwitchThe most important feature of Layer 2 is the MAC address system
Both the
Network Interface CardandSwitchoperating in Layer 2 can understand MAC addresses, and theSwitchhas the ability to specify the port to communicate with based on the MAC addressNetwork Interface Card operation
Converts electrical signals into data form
Checks the destination MAC address and source MAC address
Checks the MAC address of the Network Interface Card
If the destination MAC address matches the Network Interface Card's MAC address, it processes the data; if they differ, it discards the data
Switch operation
The Switch can determine what MAC address a terminal has and which port it is connected to through the Address learning process
Based on this data, when terminals communicate, the switch appropriately filters ports and forwards to the correct port
With the switch's proper filtering and forwarding functions, only the needed ports are used for communication, and unnecessary processing across the entire network decreases
This greatly improved Ethernet network efficiency,
And became the catalyst for the rapid increase in Ethernet-based networks!
3. Network Layer (Layer 3)
Network layer works for the transmission of data from one host to the other located in different networks.
It also takes care of
packet routingi.e. selection of the shortest path to transmit the packet, from the number of routes available.The sender & receiver's IP address are placed in the header by the network layer.
The functions of the Network layer are :
Routing
The network layer protocols determine which route is suitable from source to destination.
This function of network layer is known as routing.
Logical Addressing
In order to identify each device on internetwork uniquely, network layer defines an addressing scheme.
The sender & receiver's IP address are placed in the header by network layer.
Such an address distinguishes each device uniquely and universally.
Segment in Network layer is referred as Packet.

Network layer is implemented by networking devices such as routers
In Layer 3, logical addresses such as
IP addressesare definedTwo types of addresses are used in data communication
Layer 2's physical MAC address
Layer 3's logical IP address
Unlike MAC addresses, IP addresses can be changed to suit the user's environment
IP addresses are divided into a
network address partand ahost address partDevices or terminals that can understand Layer 3 can use network address information to
Distinguish between
their own networkandremote networksDetermine the path to reach a remote network
The device operating at Layer 3 is the Router
The Router can understand IP addresses defined in Layer 3
The Router finds the optimal path using IP addresses and forwards
packetsalong that path
4. Transport Layer (Layer 4)
Transport layer provides services to application layer and takes services from network layer.
The data in the transport layer is referred to as
Segments.It is responsible for the End to End Delivery of the complete message.
The transport layer also provides the acknowledgement of the successful data transmission and re-transmits the data if an error is found.
Transport layer is operated by the
Operating System.It is a part of the OS and communicates with the Application Layer (Layer 7) by making system calls.
Transport Layer is called as Heart of OSI model.
Layer 4 plays a different role from Layers 1~3
The lower layers (Layer 1~4) split data, attach information, and deliver it to the destination,
Layers 1~3 focus on sending signals and data to the correct location and properly generating and sending actual signals
In contrast, Layer 4 plays the role of verifying that the data is actually being sent correctly
In
Packet networks, since data is split and loaded into packets for transmission, packets may be lost or arrive out of order in transitLayer 4 is responsible for correcting these issues
When Layer 4 splits packets, it writes the sending order and receiving order in the
packet header, soIf a packet is lost, retransmission can be requested,
Even if the order is mixed up, it can be corrected
The sending order noted in the Packet is the
Sequence Number,The receiving order noted in the Packet is the
ACK Number (Acknowledgement Number)Port Numbersare used to distinguish among many applications within a device
The devices operating at Layer 4 are Load Balancers and Firewalls
These devices use the application identifier (
Port Number) visible at Layer 4 andSequence,ACK Numberinformation toDistribute load or establish security policies to pass or block packets
5. Session Layer (Layer 5)
The Session layer is responsible for establishment of connection, maintenance of sessions, authentication and also ensures security.
The functions of the session layer are :
Session establishment, maintenance and termination
The layer allows the two processes to establish, use and terminate a connection.
Synchronization
This layer allows a process to add checkpoints which are considered as
synchronization pointsinto the data.These synchronization point help to identify the error so that the data is re-synchronized properly, and ends of the messages are not cut prematurely and data loss is avoided.
Dialog Controller
The session layer allows two systems to start communication with each other in half-duplex or full-duplex.
The Session Layer, Layer 5, helps application processes at both ends
Establish connections,
Manage connections to keep them stable,
And terminate connections after work is complete
The main role of the session layer is to manage
Sessions, creating and destroying TCP/IP sessionsIt also performs recovery and retransmission for communications interrupted by errors
6. Presentation Layer (Layer 6)
Presentation layer is also called the Translation layer.
The data from the application layer is extracted here and manipulated as per the required format to transmit over the network.
The functions of the presentation layer are :
Translation
For example, ASCII to EBCDIC.
Encryption/ Decryption
Data encryption translates the data into another form or code.
Compression
Reduces the number of bits that need to be transmitted on the network.
The Presentation Layer, Layer 6, performs the function of converting data into a unified syntax format to assist communication between applications or systems with different representation methods
It acts as a kind of
translatororconverter,And this function relieves the application layer of the user system from the burden of dealing with format differences in data
Operations such as
MIME encoding,encryption,compression, andcode conversiontake place at this layer
7. Application Layer (Layer 7)
At the very top of the OSI Reference Model stack of layers, we find Application layer which is implemented by the network applications.
These applications produce the data, which has to be transferred over the network.
This layer also serves as a window for the application services to access the network and for displaying the received information to the user.
Ex: Application – Browsers, Skype Messenger etc.
Application Layer is also called as Desktop Layer.
The Application Layer, the topmost Layer 7 of OSI 7 Layers, defines application processes and performs application services
Defining the UI parts or user I/O parts of network software is the role of the application layer
There are an enormous number of application layer protocols, but representative ones include
FTP,SMTP,HTTP, andTELNET
Summary
Major Protocols and Devices by Layer
Application Layer
HTTP, SMP, SMTP, STUN, TFTP, TELNET
ADC, NGFW, WAF
Presentation Layer
TLS, AFP, SSH
Session Layer
L2TP, PPTP, NFS, RPC, RTCP, SIP, SSH
Transport Layer
TCP, UDP, SCTP, DCCP, AH, AEP
LB, Firewall
Network Layer
ARP, IPv4, IPv6, NAT, IPSec, VRRP, Routing protocol
Router, L3 Switch
Datalink Layer
IEEE 802.2, FDDI
Switch, Bridge, NIC
Physical Layer
RS-232, RS-449, V.35, S and other cables
Cable, Hub, TAP
Last updated